Wind Energy Conversion Systems
Introduction to Wind Energy Conversion Systems
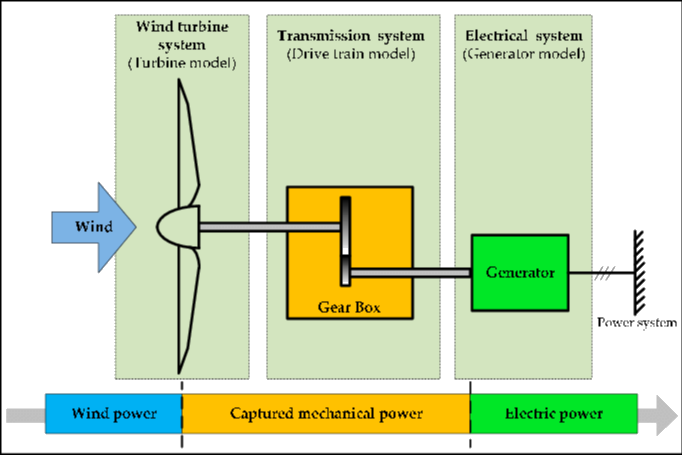
Wind energy conversion systems (WECS) are technologies that convert the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical or electrical energy. These systems utilize wind turbines, which consist of blades, a rotor, a generator, and other components. Wind energy conversion systems play a crucial role in harnessing wind power and generating clean and renewable electricity.
Question 1: What are Wind Energy Conversion Systems?
a) Systems that convert solar energy into electricity
b) Systems that convert wind energy into mechanical or electrical energy
c) Systems that convert tidal energy into electricity
Answer: b) Systems that convert wind energy into mechanical or electrical energy
Types of Wind Energy Conversion Systems
There are various types of wind energy conversion systems:
- Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT): Most common type with horizontal rotor shaft and blades rotating in the vertical plane.
- Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT): Blades rotate around a vertical axis, suitable for urban and low wind speed environments.
- Offshore Wind Turbines: Installed in bodies of water, such as oceans or lakes, to harness strong and consistent offshore winds.
- Small-Scale Wind Turbines: Designed for residential, commercial, or remote applications, generating power at a smaller scale.
Question 2: What are some of the types of Wind Energy Conversion Systems?
a) Solar panels, Tidal turbines, Geothermal systems
b) Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines, Vertical Axis Wind Turbines, Offshore Wind Turbines, Small-Scale Wind Turbines
c) Hydroelectric dams, Biomass power plants, Nuclear reactors
Answer: b) Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines, Vertical Axis Wind Turbines, Offshore Wind Turbines, Small-Scale Wind Turbines
Components of Wind Energy Conversion Systems
Wind energy conversion systems consist of several key components:
- Blades: Aerodynamic structures that capture wind energy and convert it into rotational motion.
- Rotor: The rotating part of the wind turbine that includes the blades and transfers the captured energy to the generator.
- Generator: Converts the mechanical energy from the rotor into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
- Tower: Supports the wind turbine and positions it at an optimal height for capturing wind resources.
- Nacelle: Encloses the generator, gearbox, and other components at the top of the tower.
Question 3: What are some of the key components of Wind Energy Conversion Systems?
a) Solar cells, Power inverters, Energy storage systems
b) Blades, Rotor, Generator, Tower, Nacelle
c) Wind direction sensors, Control systems, Data loggers
Answer: b) Blades, Rotor, Generator, Tower, Nacelle
Wind Energy Conversion Process
The process of converting wind energy into electrical energy involves the following steps:
- Wind Capture: The wind blows against the blades, causing them to rotate and capture kinetic energy.
- Mechanical Energy Conversion: The rotating blades transfer the captured energy to the rotor.
- Electrical Energy Conversion: The rotor’s rotational motion drives the generator, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Grid Integration: The electrical energy is transmitted to the power grid for distribution and consumption.
Question 4: What is one of the steps in the Wind Energy Conversion process?
a) Wind direction measurement
b) Mechanical energy conversion
c) Solar panel installation
Answer: b) Mechanical energy conversion
Advantages of Wind Energy Conversion Systems
Wind energy conversion systems offer numerous advantages:
- Renewable and Clean: Wind is an abundant and renewable energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
- Reduced Dependency on Fossil Fuels: Wind power reduces reliance on fossil fuels and enhances energy security.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: The wind industry creates jobs and stimulates local economies, particularly in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Wind farms can range from small-scale installations to large utility-scale projects, offering flexibility in deployment.
Question 5: What is one of the advantages of Wind Energy Conversion Systems?
a) Greenhouse gas emissions during operation
b) Increased dependency on fossil fuels
c) Job creation and economic growth
Answer: c) Job creation and economic growth
Challenges and Future Developments
Wind energy conversion systems face certain challenges and ongoing developments:
- Intermittency: Wind power is intermittent, and the variability of wind resources requires grid integration solutions and energy storage technologies.
- Environmental Considerations: Wind farms need to address potential environmental impacts on wildlife, habitats, and visual aesthetics.
- Technological Advances: Ongoing research focuses on improving turbine efficiency, reducing costs, and exploring innovative designs and materials.
- Offshore Expansion: Offshore wind energy is gaining momentum, with advancements in floating turbines and deeper water installations.
Question 6: What is one of the ongoing developments in Wind Energy Conversion Systems?
a) Environmental impacts on wildlife
b) Reduction of turbine efficiency
c) Offshore wind expansion
Answer: c) Offshore wind expansion
Case Studies
Well Done !