Geothermal Heat Pumps
Introduction to Geothermal Heat Pumps
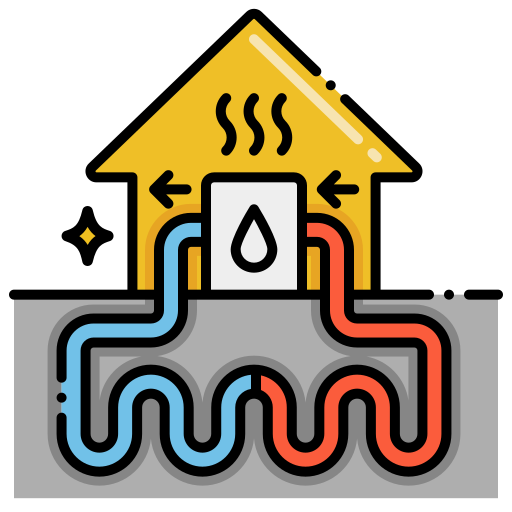
Geothermal heat pumps, also known as ground-source heat pumps, are energy-efficient heating and cooling systems that utilize the relatively stable temperature of the ground to provide indoor climate control. These systems tap into the Earth’s geothermal energy to transfer heat from the ground to a building during winter and extract heat from the building and release it into the ground during summer, providing both heating and cooling functions.
Question 1: What are Geothermal Heat Pumps?
a) Systems that convert geothermal energy into electricity
b) Systems that utilize the temperature of the ground for heating and cooling
c) Systems that generate heat and electricity from solar energy
Answer: b) Systems that utilize the temperature of the ground for heating and cooling
How Geothermal Heat Pumps Work
Geothermal heat pumps operate through the following process:
- Heat Absorption: During winter, a heat pump’s fluid circulating in underground pipes absorbs heat from the ground, which remains at a relatively constant temperature.
- Heat Transfer: The absorbed heat is transferred to the heat pump, which uses a refrigerant cycle to concentrate the heat and increase its temperature.
- Heat Distribution: The concentrated heat is then distributed throughout the building using a forced-air system or hydronic (water-based) system, providing warmth to the indoor spaces.
- Cooling Function: During summer, the process is reversed, and the heat pump extracts heat from the indoor air and transfers it to the ground, effectively cooling the building.
Question 2: How do Geothermal Heat Pumps provide heating and cooling?
a) By converting geothermal energy into electricity
b) By absorbing heat from the ground during winter and transferring heat to the ground during summer
c) By utilizing solar panels for heating and cooling purposes
Answer: b) By absorbing heat from the ground during winter and transferring heat to the ground during summer
Components of Geothermal Heat Pump Systems
A typical geothermal heat pump system consists of the following components:
- Ground Loop: A series of pipes buried underground that circulate a fluid (usually a mixture of water and antifreeze) to exchange heat with the ground.
- Heat Pump Unit: Contains the compressor, condenser, and evaporator, and is responsible for transferring heat between the ground loop and the building’s heating and cooling distribution system.
- Distribution System: The system that delivers the heated or cooled air or water to the building’s interior spaces, which can include ductwork for forced-air systems or pipes for hydronic systems.
- Thermostat: Controls the operation and temperature settings of the geothermal heat pump system.
Question 3: What are some of the components of Geothermal Heat Pump Systems?
a) Solar panels, Wind turbines, Battery storage
b) Ground loop, Heat pump unit, Distribution system, Thermostat
c) Solar collectors, Inverters, Energy storage systems
Answer: b) Ground loop, Heat pump unit, Distribution system, Thermostat
Advantages of Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps offer several advantages for heating and cooling:
- Energy Efficiency: Geothermal heat pumps are highly efficient and can provide significant energy savings compared to traditional heating and cooling systems.
- Environmental Friendly: By utilizing the Earth’s natural heat, geothermal heat pumps produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Cost Savings: Although the initial installation cost may be higher, geothermal heat pumps have lower operating and maintenance costs over their lifespan.
- Longevity and Reliability: Geothermal heat pumps have a longer lifespan compared to conventional systems and require fewer repairs.
Question 4: What is one of the advantages of Geothermal Heat Pumps?
a) Low energy efficiency
b) High greenhouse gas emissions
c) Cost savings and environmental friendliness
Answer: c) Cost savings and environmental friendliness
Challenges and Considerations
Geothermal heat pumps come with certain challenges and considerations:
- Upfront Cost: The initial installation cost of geothermal heat pump systems can be higher compared to conventional heating and cooling systems.
- Site Suitability: Suitable geological conditions and sufficient land area are necessary for the installation of ground loops.
- System Sizing and Design: Proper sizing and design of geothermal heat pump systems are crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Although geothermal heat pumps generally require less maintenance, repairs can be complex and may require professional assistance.
Question 5: What is one of the challenges of Geothermal Heat Pumps?
a) Low upfront cost
b) System sizing and design
c) High maintenance requirements
Answer: b) System sizing and design
Case Studies
Well Done !